Horizontal and Vertical Laminar Flow Hood Type
Laminar flow hood (also known as laminar flow clean benches) is an enclosed system, designed to provide a contaminant-free work environment, by directing air through HEPA-filter and exhausting it across a work surface. There are two main laminar flow hood types, which are determined by the direction of the airflow: Vertical and Horizontal. Both will guarantee protection for your samples by creating particles and a contamination-free environment. Depending on your work, you will have to decide which laminar hood is best for your task.
From Electonic to Medical, many industries are using Laminar Flow Hoods since it is suitable for a variety of applications.
What is Horizontal Laminar Airflow hood?
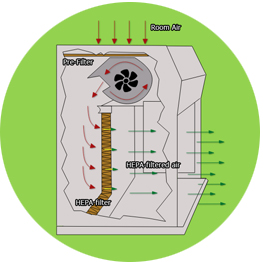
Horizontal laminar flow Hood is hood protecting the work sample from particulate contamination, using horizontal airflow direction.
The HEPA filter is positioned on the work area’s vertical rear side.
Detailed information on the process, happening in the hood:
(1) Room air enters the enclosure from the top through pre-filter
(2)turns in to horizontal direction, where passing through HEPA/ ULPA filter
(3)creates a particulate-free environment on the work surface.
(4) Filtered air exits back into the room
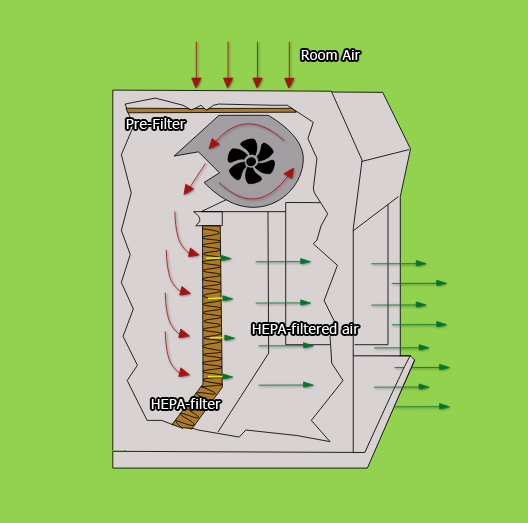
Horizontal laminar flow provides constant positive pressure between the work object and the instruments. The airflow passes without any obstruction and completely removes the particles without any turbulence. However, keep in mind that the flow of air is towards the worker. Users need to take safety precautions due to potential exposure to hazardous materials.
What is Vertical Laminar Airflow hood?
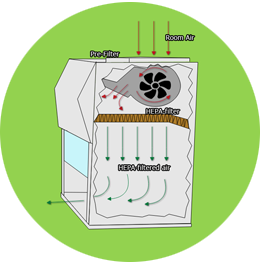
Vertical Laminar Hood protects the sample from contamination by delivering filtered air from the top of the hood, straight down onto the work surface. The HEPA filter is placed at the top of the enclosure.
Diagram
(1) Room air enters the enclosure from the top through pre-filter
(2)A blower motor pushes the air through HEPA/ ULPA into the hood in a vertical direction
(3)moves to the work surface and creates a particulate-free environment
(4)clean air exits the enclosure back into the room
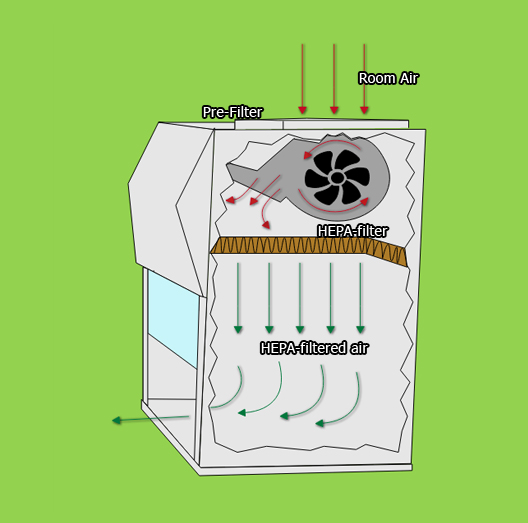
This type of laminar flow provides the airflow over the entire work area, surrounding the object with clean, filtered air. It removes particles just as horizontal laminar flow hoods, but turbulence may appear.
The downward flow sweeps the particles outside of the enclosure through holes in the base and provides better contamination protection for the user.
Laminar Flow Clean Bench / Hood Models
Clean benches have a variety of sizes and styles to provide versatile solutions for clean-critical applications.
Console model
Console laminar flow can be vertical or horizontal airflow direction.
- Removes air from under the work surface
- The motor is placed under the work surface, which makes it easier to access
Bench models
Table Top Models
These models are space-saving and easy to clean. They have underneath opening, which can be used for carts, trash, or storage. It can be Vertical or Horizontal. Table top models control airborne contamination within a small space.
Which Laminar Flow Hood type to choose for your application?
Deciding which laminar flow hood type to choose for your application can be difficult. The decision depends on:
- what your processes are,
- operator safety,
- work surface required,
- characteristics of your samples,
- the equipment used in the process
- the size of the area you are placing it
Understanding the difference of each type could be essential for choosing the correct laminar flow for your application.
Vertical and horizontal airflow benches each have pros and cons when it comes to keeping objects contamination-free. The most important is to avoid creating turbulence around the material you are working with it. Turbulent flow can be disturbing to work that requires a dust-free environment.
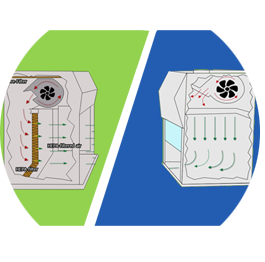
Vertical vs. Horizontal Laminar Flow Hoods

Horizontal and vertical laminar flow hood types have the same goal: to create free of particles and contamination environment to protect your product.
How we know already they are different by airflow direction:
- Vertical flow hoods produce a constant airflow from the top down to the work surface.
- Contrariwise: the Horizontal blows the air from the back towards the work surface.
Horizontal Laminar Flow Pros
• Low possibility of turbulence effect
• Hand are downstream the airflow and reduce the risk of contamination from the user
• The horizontal direction of the airflow blows most of the particles out from the unit
• Bigger workspace
• Well suited if your work requires directly over the work area.
Horizontal laminar flow Cons
• The air flows horizontally and may blow contaminated particles into the face of the worker.
• It can create turbulence with larger equipment and samples.
• Services or filter changes require rear access, so the hood may have to be re-positioned.
• The HEPA filter is located on the backside of the work surface and while working, it easy to damage.
Vertical laminar flow Pros
• The contaminated air does not blow directly into the worker.
• Can be used with larger equipment and tools
• A sash works as a barrier and protects the air blowing directly at the worker’s face
• Less turbulence when working with large objects or equipment
Vertical laminar flow Cons
• It obstructs the airflow when placing hand or stack items
• It’s required free space at the top
• The turbulent effect may occur at the work surface because of air striking
When your application requires minimal turbulence and maximum contamination control, Horizontal laminar hoods are the best choice. They are ideal for work with small objects and equipment.
Horizontal laminar flow hood is right for your work if:
• You need minimal turbulence on the work surface.
• You are using small equipment that will not cause airflow disturbance.
• You need better contamination protection.
When your application requires the use of large equipment, Vertical laminar flow hoods have less turbulence and pushing particles down and away from the operators and work surface.
Choose a vertical laminar flow hood when:
• You need larger workspace – there is greater width, depth and height available on the work surface.
• You use large equipment on the work area – Less turbulence is when hitting large items within the flow is
• If you use a microscope or any other sample, raised from the work surface, the vertical flow hood will optimize the evacuation of particles from the point of use.
• When you need a quality airflow over the entire surface of your enclosure
What is the difference between a fume hood and laminar flow?
A Note On Bio-hazards And Laminar Flow Hoods Types
Use laminar flow hoods for working with non-hazardous powders or nuisance odors being generated on the work surface.
When it comes to laminar flow hoods, remember that they are not safe to use with bio-hazards. Only an approved system of containment, including Biosafety Cabinets Type A2 Class II, is intended in procedures that require containment at Bio-Safety Level two or three.
Keep in mind that the protection of samples and parts from contamination within the enclosure is the primary purpose of laminar flow hoods. Clean Benches do not protect the user from toxic chemicals or infectious materials. With this in mind, make sure to wear complete safety gear every time you work with laminar flow hoods types.